Do more Megapixels mean better photo quality?
Modern smartphones often perform the role of a camera that is always with you. Thus, before buying a new device, a potential buyer spends a lot of time on choosing a camera. You would often hear that the image quality depends on the number of megapixels (MP). Still, however disappointing it may sound for some of you, this opinion not true.
To find out which camera specifications do influence its capacity and image quality, we recommend that you learn more about them.
Camera Main Characteristics and Features
Aperture
When buying a smartphone, choose a camera with a low f-number.
The lens aperture is an opening through which light travels to the sensor. F-number is denoted with a small Latin letter f. The lower the f-number, the wider the lens aperture and the more light that passes through it. For example, a camera with the aperture of f/5.6 will allow less light than a camera with f/2.0 aperture. Thus, in low light, a camera with the small aperture value will give the best results. Technical specifications always indicate the maximum value of f-number.
Focal Length
The Focal Length (FL) is the distance from the optical center of the lens to the image plane (the camera matrix center). With smartphone cameras, it is the distance to the image sensor.
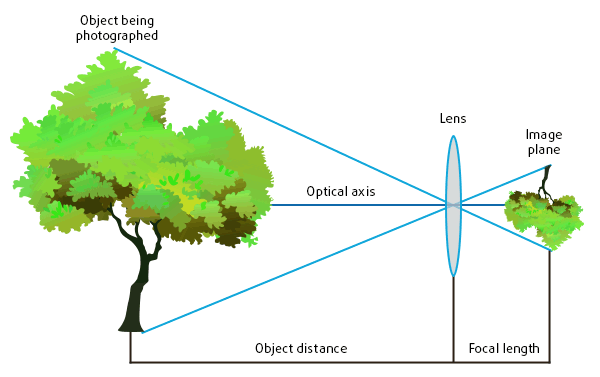
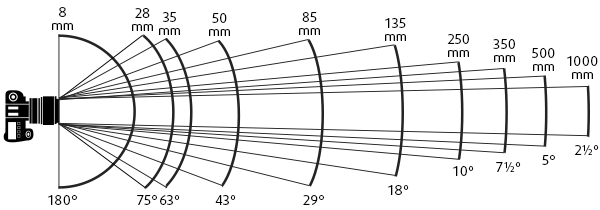
When zooming is performed, the optical center of a zoom lens changes, thus changing the focal length value. The FL value informs us about the shooting angle.
Effective Focal Length is a conditional characteristic, which informs you about the angle of view and the width of lens.
It is customary for photographers to calculate the angle of view based on the focal length. To find out the FL, look at the effective focal length of the lens, which takes into account the sensor size and displays it in 35 mm equivalent.
For example, iPhone 6 and iPhone 6 Plus have wider angles of view than Galaxy S5 because 29 mm correspond to 73.4 °, while 31 mm – to 69.8 °.
The producers often equip the front camera with the lens that has a shorter focal length than the main camera lens. This is done to improve video calls image quality and reduce geometrical aberrations.
To find out your camera zoom, divide the maximum focal length by the minimum. For example, 240 ÷ 24, will give us a 10x zoom.
Matrix size
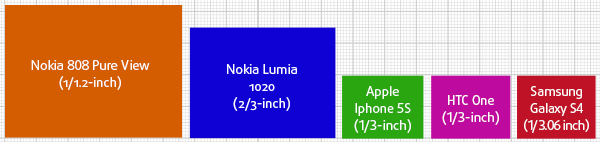
The sensor (matrix) size plays an important role in the performance of the camera. This is the case when the size does matter. The larger the matrix, the higher the image quality. The most important characteristic of the sensor is the size of pixels.
Pixels are measured in micrometers (µm) or microns (μ). Today, almost all manufacturers indicate this characteristic, since customers are aware of its importance and pay attention to it.
The pixel size directly affects the image quality in various environments, including the camera performance in low (poor) lighting.
The ratio of the pixel size and its ability to collect light is directly proportional. The larger the pixel size (photodiode, the aperture ratio of pixels), the more light it collects.
Modern smartphones, except for camera phones, have roughly the same matrix size. Each element corresponds to a single point in the image. The present-day matrices are made up of millions of pixels. For example, there are cameras taking pictures with a maximum resolution of 3888 to 2592 points. Multiply these two numbers and you will get the number of pixels - about 10 million. Then in the technical characteristics of the camera, you will find information on 10 MP resolution.
Only recently, the number of megapixels did matter when taking a photo. Indeed, several years ago, a camera phone resolution was so small (0.3 megapixel) that such a picture was not even printable.
Today, even 40-megapixel cameras are produced, but it is just marketspeak for those unfamiliar with smartphone specifications. So, if the camera specifications show a large number of megapixels, do not forget to check the physical size of the matrix, because manufacturers quite often forget to specify it. The truth is that the more pixels are at the matrix, the smaller they are. Consequently, such a matrix gathers less light, which results in increased "digital noise" in the image. For example, a camera with the resolution of 12 megapixels and the matrix of 4/3 " will take pictures of a much higher quality than a 40-megapixel device with the matrix of 2/3". The sensor size is indicated in inches, for example, 1 / 2,3 "(6.17 × 4.55 mm), 4/3" (17.30 × 13.00 mm).
If the manufacturer has not indicated the matrix characteristics, then you can look for the module model in camera specifications and get all the necessary information based on the module.
Image Stabilization
When taking pictures with a smartphone, you often hold it in hands. In good light, the camera sets a slow shutter speed, so even when your hand wobbled a bit, the image quality will not suffer. However, with pictures taken in a dark room or in a street at night, the slightest hand movement will make the image blurred. It happens because the camera slows the shutter speed in bad light to compensate for the lack of light.
To fix this problem, manufacturers supply all modern cameras with image stabilization.
Image Stabilization is another significant characteristic of modern phone cameras. There are 2 types of stabilization: optical and digital.
With optical image stabilization, the camera captures images when the photographer’s hand moves. The principle is to move the lens elements in the direction opposite to the movement. Such balancing helps to make the image sharper.
With digital stabilization, they use software settings in the real time to compensate for the movement. Not the whole matrix area is used to record the video and save photos, and the free space is used to transmit or move the image and compensate for the motion.
For photos, it is advisable to choose a camera with optical image stabilization, because it is more efficient and does not change the frame resolution. However, if you are planning to shoot videos with your smartphone, it is better to choose a device with digital stabilization.
Flash
"Flash is not a characteristic!" you might say. However, you should not forget about the flash, because this is what can help you get a superb picture in low light.
All modern smartphones use two types of built-in flash:
- Xenon flash shines brightly and colors come natural. This flash cannot be used for constant illumination; also, its cost value is high and the size does not fit the size of smartphones. At present, they practically never use a xenon flash in smartphones;
- LED flash is characterized by its energy efficiency and high luminous efficiency. The main advantage of LED flash is that it can be used as a flashlight, which is not possible with a xenon flash.
In expensive smartphone models, manufacturers can install two flashes at the same time - LED and xenon. The flash choice will depend on personal preferences and shooting conditions.
In this article, we talked about the main characteristics of a smartphone camera. Now you know which camera settings you should pay attention to when choosing a smartphone.
If you already have a smartphone, but for some reason its camera does not work, do not worry and visit our website. You will be happy to see affordable prices and a wide range of smart phone cameras at our online store All Spares.